Developing a website involves several steps, which can be summarized as follows:
Things Should Consider Developing a Website:
Purpose and Goals:
Determine the purpose and goals of your website. What do you want to achieve with your website? Who is your target audience? State clearly your mission and why you want to have a website. Either it’s for education purposes or business services. State clearly your mission to have a website.
Content Strategy:
Create a content strategy for your website. Determine what content will be included on your site. How it will be organized, and how it will be presented. Therefore, it involves planning, creating, and managing content that is relevant. Useful and engaging for the website’s target audience.
A content strategy can help to improve a website’s search engine optimization (SEO) by incorporating relevant keywords into the content.
Design:

Develop a design that is visually appealing and easy to navigate. A website design is a critical component of its success. Therefore, careful consideration of some factors can help ensure that the design effectively communicates the brand messages and engages the target audience.
Here are some key things to consider when developing a website design:
Purpose and Audience:
Understand the purpose of the website and who the target audience is. The design should reflect the needs and preferences of the target audience.
Branding:
The design should reflect the brand identity of the organization. Including colors, logos, and overall style.
Layout and Navigation:
The layout should be well-organized and easy to navigate. Allowing users to quickly find the information they need.
Visual Appeal:
The design should be visually appealing and use high-quality images, graphics, and typography.
Consistency:
The design should be consistent across all pages. Ensuring a cohesive user experience.
Responsiveness:
The design should be responsive, adapting to different screen sizes and devices.
Accessibility:
Website accessibility involves designing and developing websites that can be used by people with disabilities. Including those who are blind, visually impaired, deaf, hard of hearing, or have mobility impairments. The design should be accessible to all users, including those with disabilities.
Loading Speed:
The design should be optimized for fast loading speeds, minimizing page load times.
User Experience:
The design should prioritize the user experience, making it easy and enjoyable for users to interact with the website.
Scalability:
The design should be scalable, allowing for future updates and changes to the website without compromising the overall design and user experience.
Domain Name:
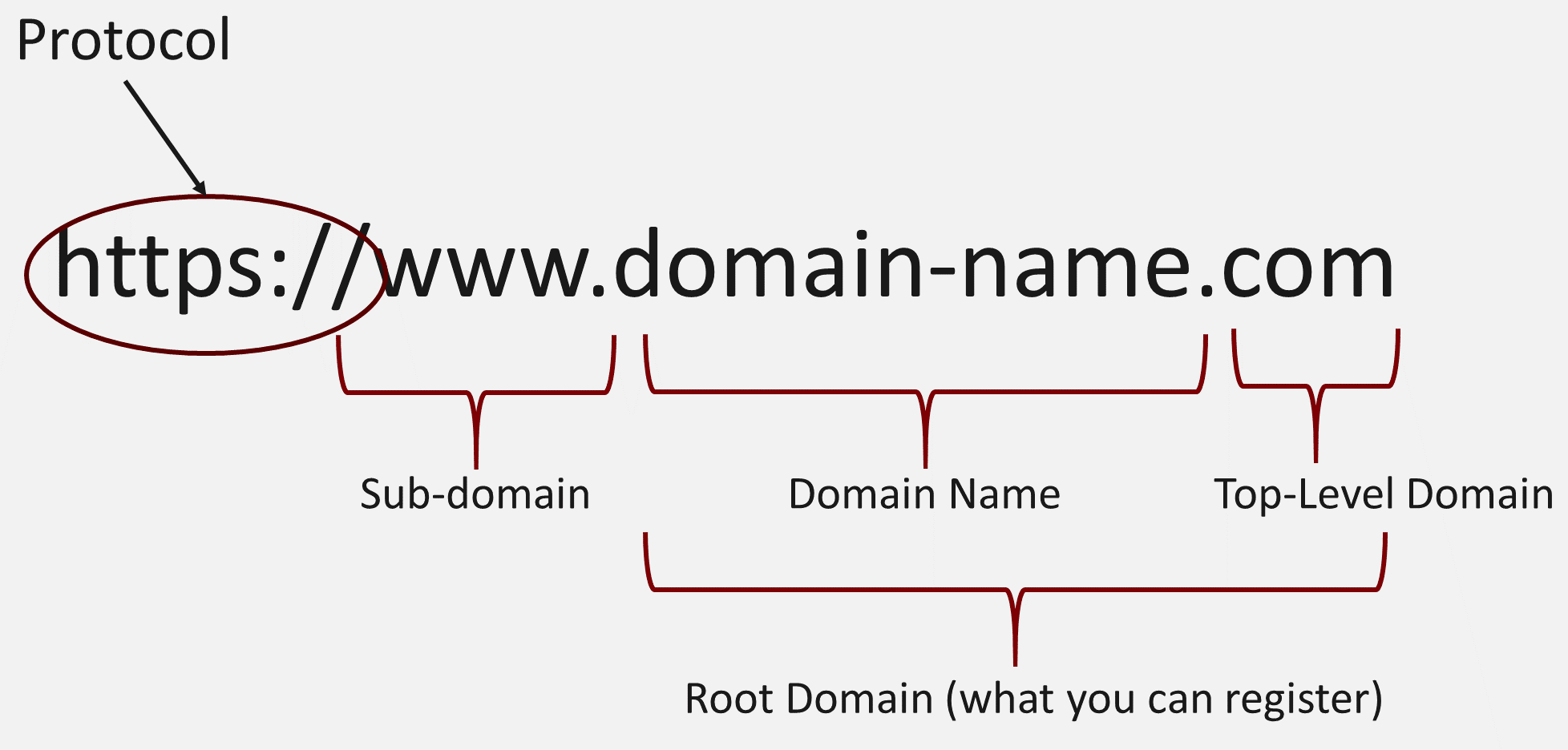
Choose a domain name that is easy to remember and relevant to your website’s purpose.
Website Hosting:
Select a reliable hosting provider that can handle your website’s traffic and offer security features.
Search Engine Optimization (SEO):
Optimize your website for search engines by incorporating relevant keywords into your content and meta tags.
Mobile Responsiveness:
Ensure that your website is mobile-responsive and looks good on different devices, including smartphones and tablets.
Usability:
Make sure that your website is user-friendly and easy to navigate. Consider conducting usability testing to identify and address any issues.
Website Security:

Website security should be an essential part of any website development and maintenance plan. Therefore, website security is crucial for protecting sensitive data and ensuring the safety of both the website owner and its users.
Implement security measures to protect your website from hacking, malware, and other threats. Here are some of the top important factors for website security:
SSL/TLS Certificate:
Implementing an SSL/TLS certificate on a website provides a secure, encrypted connection between the website and its users.
Regular Software Updates:
Keeping software and plugins up-to-date reduces the risk of vulnerabilities being exploited by attackers.
Strong Passwords:
Encouraging the use of strong passwords by website users can prevent unauthorized access to sensitive information.
Two-Factor Authentication:
Implementing two-factor authentication provides an additional layer of security to protect user accounts.
User Permissions:
Limiting user access to certain areas of the website can prevent unauthorized changes or access to sensitive information.
Firewall Protection:
Implementing a firewall can help prevent unauthorized access to the website and its data.
Backup and Recovery Plan:
Having a backup and recovery plan in place can help minimize data loss. However, it ensures the website can be quickly restored in the event of a security breach.
Security Monitoring:
Regularly monitoring the website for security threats can help detect and prevent attacks before they cause damage.
Malware Scanning:
Regularly scanning the website for malware and viruses can help identify and remove any malicious code. That could be used to compromise security.
Regular Security Audits:
Conducting regular security audits can help identify and address vulnerabilities before they can be exploited by attackers.
Analytics:
Install analytics software to track your website’s traffic, user behavior, and performance. Use this information to make informed decisions about future updates and improvements.
